Measure temperature - Virtual IoT Hardware
In this part of the lesson, you will add a temperature sensor to your virtual IoT device.
Virtual Hardware
The virtual IoT device will use a simulated Grove Digital Humidity and Temperature sensor. This keeps this lab the same as using a Raspberry Pi with a physical Grove DHT11 sensor.
The sensor combines a temperature sensor with a humidity sensor, but in this lab you are only interested in the temperature sensor component. In a physical IoT device, the temperature sensor would be a thermistor that measures temperature by sensing a change in resistance as temperature changes. Temperature sensors are usually digital sensors the internally convert the resistance measured into a temperature in degrees Celsius (or Kelvin, or Fahrenheit).
Add the sensors to CounterFit
To use a virtual humidity and temperature sensor, you need to add the two sensors to the CounterFit app
Task - add the sensors to CounterFit
Add the humidity and temperature sensors to the CounterFit app.
-
Create a new Python app on your computer in a folder called
temperature-sensorwith a single file calledapp.pyand a Python virtual environment, and add the CounterFit pip packages.⚠️ You can refer to the instructions for creating and setting up a CounterFit Python project in lesson 1 if needed.
-
Install an additional Pip package to install a CounterFit shim for the DHT11 sensor. Make sure you are installing this from a terminal with the virtual environment activated.
pip install counterfit-shims-seeed-python-dht -
Make sure the CounterFit web app is running
-
Create a humidity sensor:
-
In the Create sensor box in the Sensors pane, drop down the Sensor type box and select Humidity.
-
Leave the Units set to Percentage
-
Ensure the Pin is set to 5
-
Select the Add button to create the humidity sensor on Pin 5
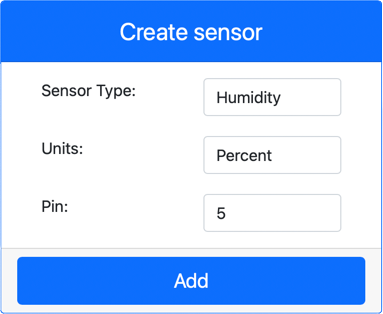
The humidity sensor will be created and appear in the sensors list.
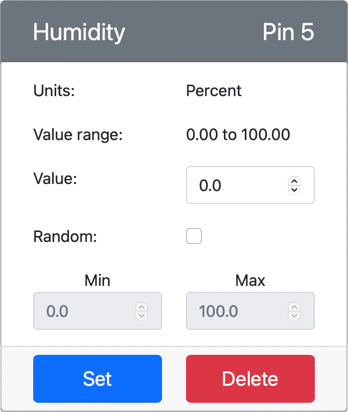
-
-
Create a temperature sensor:
-
In the Create sensor box in the Sensors pane, drop down the Sensor type box and select Temperature.
-
Leave the Units set to Celsius
-
Ensure the Pin is set to 6
-
Select the Add button to create the temperature sensor on Pin 6
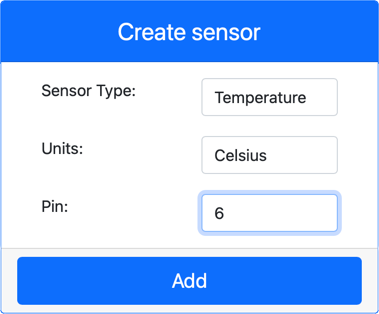
The temperature sensor will be created and appear in the sensors list.
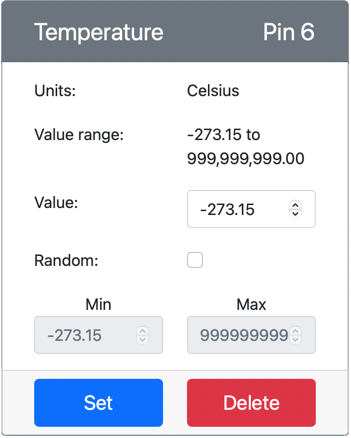
-
Program the temperature sensor app
The temperature sensor app can now be programmed using the CounterFit sensors.
Task - program the temperature sensor app
Program the temperature sensor app.
-
Make sure the
temperature-sensorapp is open in VS Code -
Open the
app.pyfile -
Add the following code to the top of
app.pyto connect the app to CounterFit:from counterfit_connection import CounterFitConnection
CounterFitConnection.init('127.0.0.1', 5000) -
Add the following code to the
app.pyfile to import the required libraries:import time
from counterfit_shims_seeed_python_dht import DHTThe
from seeed_dht import DHTstatement imports theDHTsensor class to interact with a virtual Grove temperature sensor using a shim from thecounterfit_shims_seeed_python_dhtmodule. -
Add the following code after the code above to create an instance of the class that manages the virtual humidity and temperature sensor:
sensor = DHT("11", 5)This declares an instance of the
DHTclass that manages the virtual Digital Humidity and Temperature sensor. The first parameter tells the code the sensor being used is a virtual DHT11 sensor. The second parameter tells the code the sensor is connected to port5.💁 CounterFit simulates this combined humidity and temperature sensor by connecting to 2 sensors, a humidity sensor on the pin given when the
DHTclass is created, and a temperature sensor that runs on the next pin. If the humidity sensor is on pin 5, the shim expects the temperatures sensor to be on pin 6. -
Add an infinite loop after the code above to poll the temperature sensor value and print it to the console:
while True:
_, temp = sensor.read()
print(f'Temperature {temp}°C')The call to
sensor.read()returns a tuple of humidity and temperature. You only need the temperature value, so the humidity is ignored. The temperature value is then printed to the console. -
Add a small sleep of ten seconds at the end of the
loopas the temperature levels don't need to be checked continuously. A sleep reduces the power consumption of the device.time.sleep(10) -
From the VS Code Terminal with an activated virtual environment, run the following to run your Python app:
python app.py -
From the CounterFit app, change the value of the temperature sensor that will be read by the app. You can do this in one of two ways:
-
Enter a number in the Value box for the temperature sensor, then select the Set button. The number you enter will be the value returned by the sensor.
-
Check the Random checkbox, and enter a Min and Max value, then select the Set button. Every time the sensor reads a value, it will read a random number between Min and Max.
You should see the values you set appearing in the console. Change the Value or the Random settings to see the value change.
(.venv) ➜ temperature-sensor python app.py
Temperature 28.25°C
Temperature 30.71°C
Temperature 25.17°C -
💁 You can find this code in the code-temperature/virtual-device folder.
😀 Your temperature sensor program was a success!